High Protein Full Day of Eating
WHY HIGH IN PROTEINS?
A high protein intake is crucial when lifting weight to give to your body what it needs to repair broken muscle cells.
“To maximize muscle protein accretion with resistance exercise, daily protein intakes should be ~1.6 g/kg/day and up to 2.2 g/kg/day. This intake can be achieved by ingesting 3 meals, each containing ~0.53 g/kg protein, or 4 meals containing ~0.4g/kg protein.” [1]
The optimal intake can even go as much as 2.3–3.1 g/kg/day when trying to retain muscle mass in a caloric deficit. [1]
The following will present what a day of eating would look like for someone who tries to gain muscle mass in a caloric deficit and is about 75 kg in weight. His protein intake according to the study should be between 120-165 g. The day is divided into 4 meals with even distributed protein intake to optimize absorption.
MEAL 1
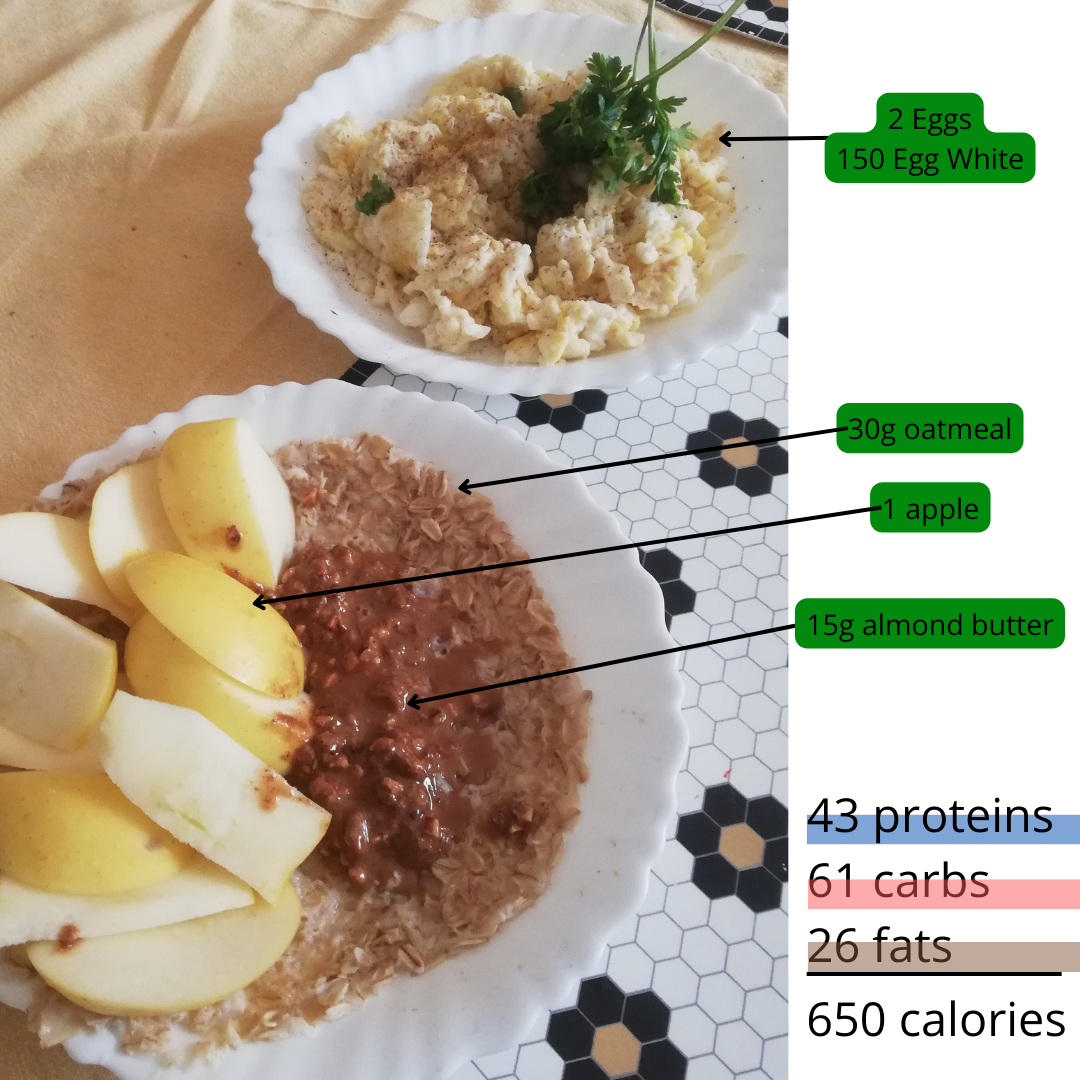

Consists of:
- 2 whole eggs and 150 g of egg white. This accounts for the majority of proteins in the meal. It’s a high volume protein intake, perfect for when trying to lose weight because it will keep you full longer.
- 30 g of oatmeal microwaved with water. Oatmeal is a good carbohydrate source because it’s glycemic index is lower which means that you will have a sustain gain in energy instead of a quick peak. “Foods with GI values of less than 55 are considered low GI, 56 to 69 are mid-range GI, and those with GI values greater than 70 are defined as high GI foods.” [2] The one for grain oatmeal is 51. [2]
- 1 apple for fibers and minerals.
- 15 g of almond butter for healthy fats. Almond butter is better because compared to peanut butter it has 2 times less saturated fat that can raise cholesterol. [3]
MEAL 2

Consists of a tacos recipe:
- 81 g of tacos shell.
- 150 g of lean beef to avoid excess fat intake. Beef has some iron which is important for weightlifters since it was shown it can decrease when training. [4] Therefore, beef consumption at least 1 time a week can help maintaining adequate iron level.
- 1/2 avocado, a healthy fat intake option. It reduces cholesterol and prevents cardiovascular diseases. [5]
- 2 tbsp salsa.
- veggies such as tomatoes, lettuce, onion and pepper.
MEAL 3
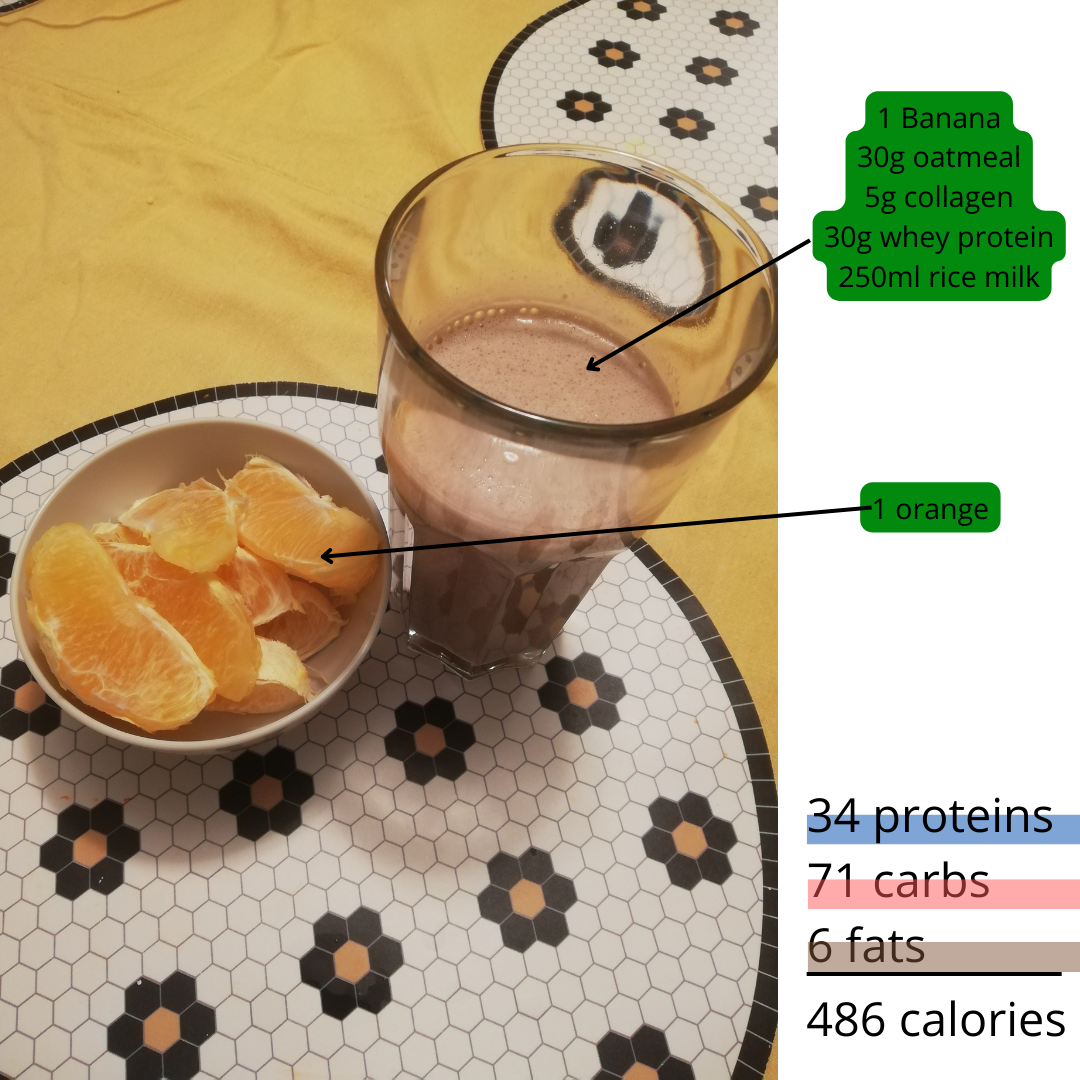

Consists of a protein shake as an easy meal option:
- 1 banana.
- 30 g oatmeal.
- 5 g of collagen as supplementation which is a must for weightlifters who do a lot of micro-traumas to joints and ligaments. People should consume between 2.5-10 g of collagen peptides per day which has been shown to not be the case in the standard American diet. [6]
- 250 ml of rice milk to increase carbs intake.
- 1 orange.
MEAL 4

Consists of:
- 150 g of multigrain bread. This is about 4 medium sized slices of bread. Favor multigrain instead of plain bread since it has a lower glycemic index and higher fiber intake.
- 30 g of guacamole as a spread over bread.
- 30 g of hummus again as a spread over bread.
- 60 g of tuna. It is an easy protein intake option since it’s canned and quick to eat. However, tuna and other bigger fish have a high mercury concentration in their meat. It was shown that high mercury concentration in the human body has reproductive and neurological side effects. Therefore, the recommendation is to only eat 3 times per week meats with higher mercury concentration such as tuna and salmon. [7]
FINAL THOUGHTS
This bring us to a total of 2564 calories for the day with macros:
- 154 g of proteins
- 272 g of carbs
- 95 g of fats
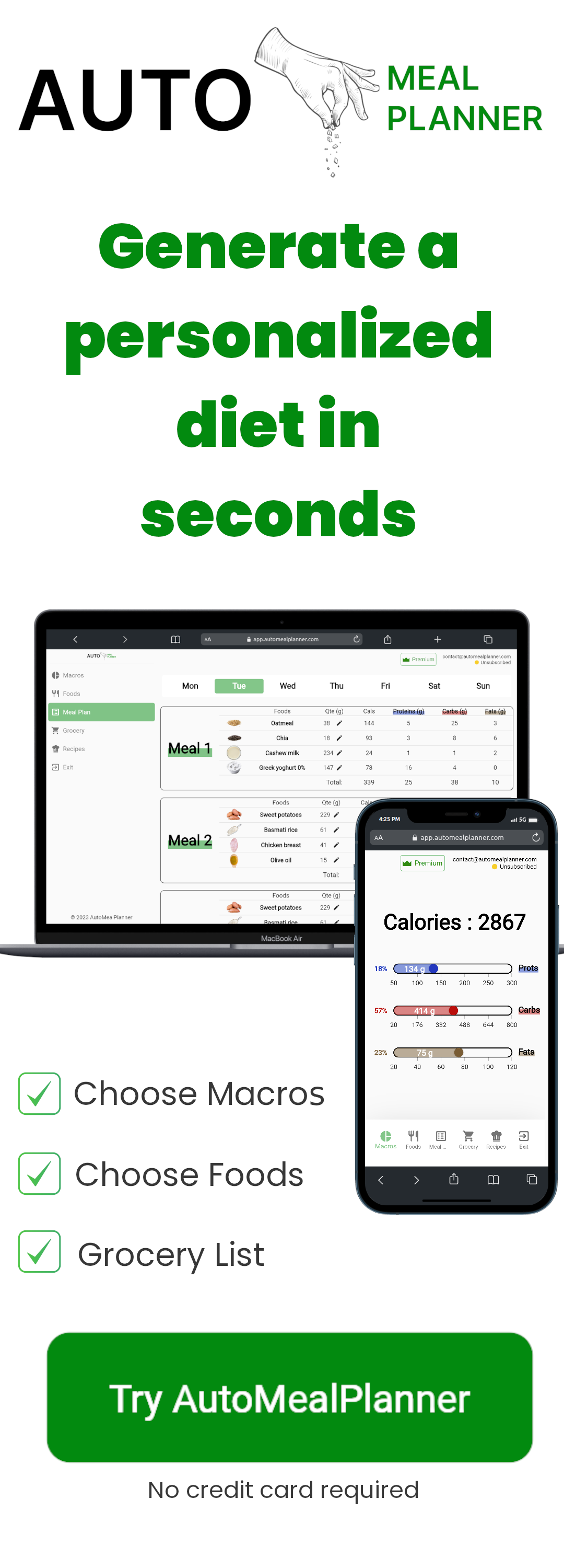
Don’t have an idea of how to generate a high protein diet or need inspiration? You can look at AutoMealPlanner app which provides a custom diet given caloric and macros requirements in seconds.
REFERENCES
- Stokes, T., Hector, A. J., Morton, R. W., McGlory, C., & Phillips, S. M. (2018). Recent perspectives regarding the role of dietary protein for the promotion of muscle hypertrophy with resistance exercise training. Nutrients, 10(2), 180.
- Zhang, K., Dong, R., Hu, X., Ren, C., & Li, Y. (2021). Oat-based foods: Chemical constituents, glycemic index, and the effect of processing. Foods, 10(6), 1304.
- Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/almond-butter-peanut-butter#comparison
- Deruisseau, K. C., Roberts, L. M., Kushnick, M. R., Evans, A. M., Austin, K., & Haymes, E. M. (2004). Iron status of young males and females performing weight-training exercise. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 36(2), 241-248.
- Duarte, P. F., Chaves, M. A., Borges, C. D., & Mendonça, C. R. B. (2016). Avocado: characteristics, health benefits and uses. Ciência rural, 46, 747-754.
- Paul, C., Leser, S., & Oesser, S. (2019). Significant amounts of functional collagen peptides can be incorporated in the diet while maintaining indispensable amino acid balance. Nutrients, 11(5), 1079.
- Murata, Y. (2018). Tuna Consumption and Tuna Mercury Concentration-Implications for Human Health (Doctoral dissertation, UC Santa Cruz).